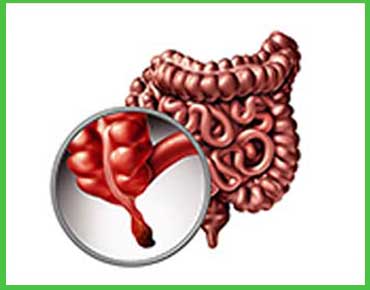
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix, which occurs suddenly and is very painful. The appendix is a small pouch that attaches to the large intestine. The pain starts mild but typically very quickly develops into severe pain which is felt usually in the lower right abdomen. The condition being untreated can make the appendix burst, leading to life-threatening infections. Appendicitis happens to both children and adults and requires immediate medical attention. The common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and fever. Surgery, appendectomy, is the only treatment for it that takes care of complications. Early diagnosis helps to avoid rupture and further complications. If you experience persistent stomach pain, don't ignore it; this is a medical emergency demanding urgent action.
The main treatment of appendicitis is an operation called an appendectomy, in which the diseased appendix is removed. This can be done through open surgery or laparoscopic surgery (minimally invasive surgery for faster recovery). In the early days of the disease, treatment can also include antibiotics against the infection before surgery. If the appendicitis ruptures, urgent surgery and drainage of the infection are needed. Post-operation, pain control, hydration, and rest are important for recovery. Further, the earlier it is diagnosed and treated, the fewer the chances of developing complications such as peritonitis, thereby allowing smooth recovery.
